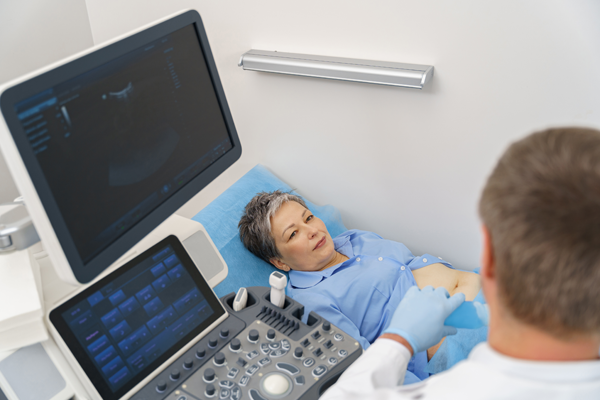
Medical imaging plays a critical role in ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment planning in healthcare. One of the most commonly used methods in this field is ultrasonography, also known as ultrasound imaging. Since it is a non-invasive and radiation-free method, it prioritizes both patient comfort and safety. Sonography allows for detailed examination of organs, tissues, and fluid accumulations in the body. In this article, we will discuss what sonography is, its applications, scanning process, and advantages in detail.
1. What is Ultrasonography?
Ultrasonography is a medical imaging method that uses sound waves. These sound waves reflect off the organs in the body and are converted into images by the device. The obtained images are used by doctors to evaluate the structure, size, and possible pathologies of organs.
The main advantage of ultrasound imaging is that it does not involve radiation and is completely safe. It has a wide range of applications, from pregnancy monitoring and internal organs to prostate-uterus-ovaries, heart and vascular evaluations, liver and kidney assessments, as well as muscles and joints.
2. Applications of Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography is a versatile method widely used in medical diagnosis. Its main applications include:
- Pregnancy Monitoring: Used to observe fetal development, determine gestational age, and detect possible anomalies.
- Abdominal Organs: Ideal for assessing the structure and functions of organs such as the liver, kidneys, spleen, and pancreas.
- Reproductive Organs: Used in examinations of the uterus and ovaries in women, and the testes and prostate in men.
- Heart and Blood Vessels: Doppler ultrasound evaluates heart valves and vessels, analyzing blood flow.
- Muscles and Joints: Sports injuries, muscle tears, or joint problems can be detected with ultrasound.
- Thyroid and Breast: Thyroid nodules, breast masses, or cysts can be examined by ultrasonography.
3. Types of Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography varies depending on its purpose and the area being examined:
- Transthoracic Ultrasound: Performed through the chest to examine the heart and chest cavity.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Performed vaginally to provide a more detailed view of female reproductive organs.
- Transrectal Ultrasound: Used in the evaluation of the prostate and rectal area.
- Doppler Ultrasound: Measures the speed and direction of blood flow, helping to detect vascular blockages.
- 3D and 4D Ultrasound: Especially used in pregnancy follow-ups to obtain three-dimensional and real-time images of the fetus.
4. How is Ultrasonography Performed?
Ultrasound scanning is non-invasive and usually painless. The procedure is performed through the following steps:
- Preparation: Certain types of ultrasound may require fasting or a full bladder. For example, abdominal ultrasound often requires 6–8 hours of fasting, while pelvic ultrasound may require a full bladder.
- Positioning: The patient is placed in a suitable position depending on the area to be examined. For abdominal ultrasound, lying on the back is usually sufficient, while specific positions are required for transvaginal ultrasound.
- Gel Application: A gel is applied between the probe and the skin to ensure contact. This gel improves sound wave transmission and image quality.
- Imaging: The ultrasound probe is moved over the skin to scan the organs, and the images are displayed on a computer.
- Analysis: The images are examined by a radiologist or relevant specialist, and a report is prepared.
5. Advantages of Ultrasonography
The most important advantages of ultrasonography are:
- Safe and Non-Invasive: No entry into the body is required, and it does not involve radiation.
- Painless: Most patients do not feel any discomfort during ultrasound.
- Fast and Practical: The procedure usually takes 15–30 minutes, and results can be obtained quickly.
- Repeatable: It can be safely repeated at short intervals if necessary.
- Detailed Imaging: Highly effective in visualizing soft tissues and fluid accumulations.
6. Before and After Ultrasonography
- Before: Some examinations may require fasting or a full bladder. Patients should follow medical instructions regarding medication and wear comfortable clothing.
- After: In most cases, no special procedure is needed. Patients can return to their daily activities immediately.
7. Who is Ultrasonography Suitable For?
Ultrasonography can be performed on nearly all age groups and various health conditions, particularly for:
- Pregnant women
- Patients with abdominal, pelvic, heart, or thyroid problems
- Individuals with sports injuries or muscle issues
- People at risk of vascular blockage
Conclusion
Ultrasonography is a safe and effective method that plays a critical role in both diagnosis and follow-up in modern medicine. Thanks to its non-invasive nature and lack of radiation exposure, it offers a comfortable imaging option for patients. With its wide range of applications— from pregnancy monitoring to heart and vascular diseases, abdominal organs to muscle and joint problems—ultrasonography is an indispensable tool for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
İstersen sana bu metnin Arapça ve Rusça çevirilerini de hazırlayayım mı?