Osteoporosis, also known as bone loss, is a condition that occurs when bone density decreases, making bones fragile and more prone to fractures. Aging, nutritional deficiencies, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic factors can increase the risk of osteoporosis. So, which medical department should individuals with suspected osteoporosis visit?
Which Department Should You Visit for Osteoporosis?
The primary medical specialties for osteoporosis are Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PMR) or Orthopedics and Traumatology. However, depending on the underlying causes of the disease, other specialties may also be involved.
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PMR): This department specializes in diagnosing and treating osteoporosis. Bone density tests can be performed here, and appropriate exercise programs may be recommended.
- Orthopedics and Traumatology: If osteoporosis leads to fractures or other skeletal problems, an orthopedic specialist should be consulted.
- Endocrinology: Since hormonal imbalances can cause osteoporosis, this department is especially important for postmenopausal women and patients with thyroid disorders.
- Internal Medicine: For general health assessments and risk factor evaluations related to osteoporosis, an internal medicine specialist can be consulted.
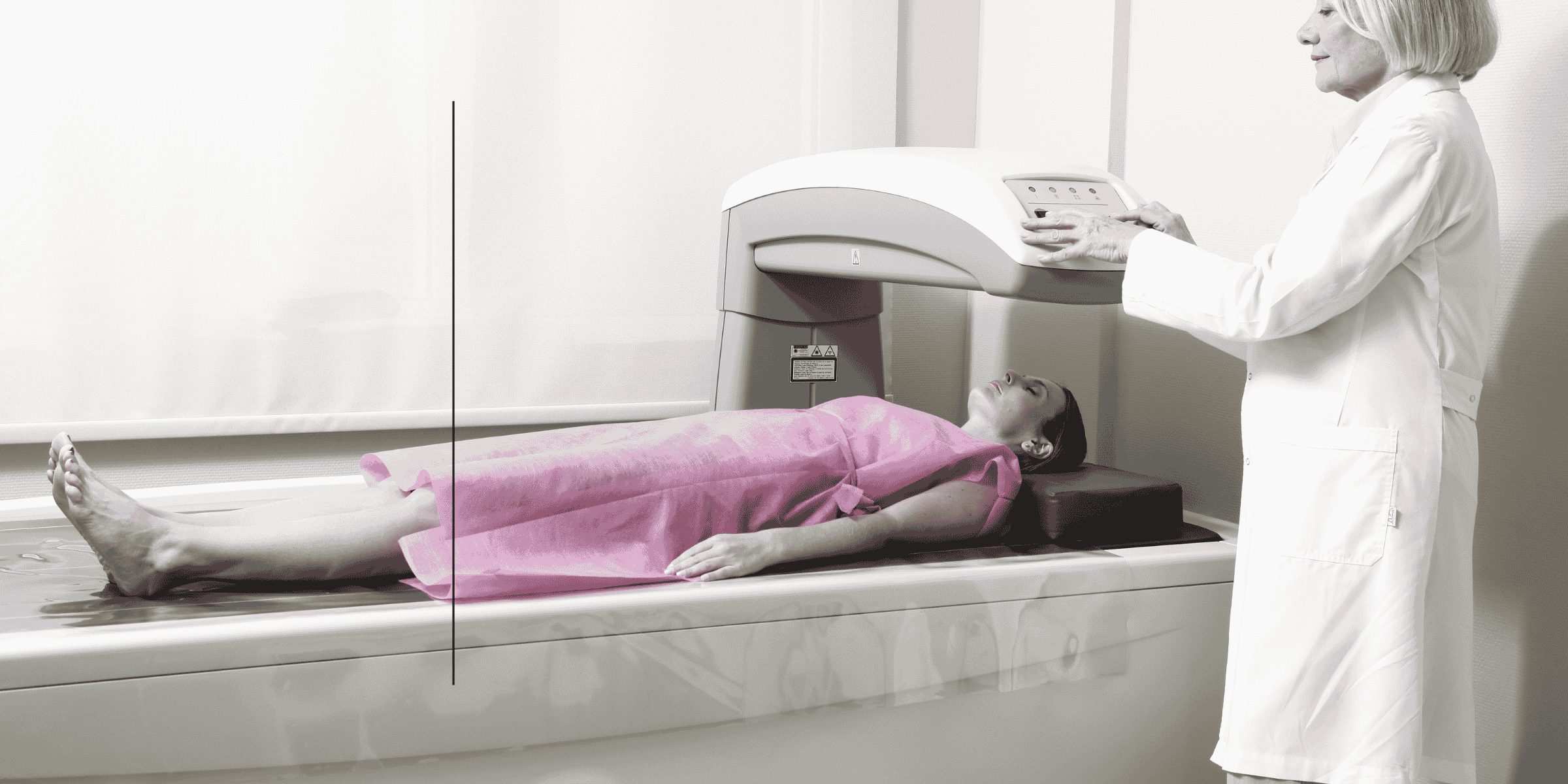
How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed?
Osteoporosis is typically diagnosed using bone mineral density testing (DEXA scan), which measures bone density and assesses fracture risk. Additionally, blood and urine tests can help identify underlying causes of osteoporosis.
How Is Osteoporosis Treated?
The goal of osteoporosis treatment is to prevent bone loss, increase bone density, and reduce fracture risk. Treatment generally includes:
- Nutrition: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential. Consuming milk, yogurt, cheese, leafy green vegetables, and fish supports bone health.
- Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises (such as walking and light weight training) help increase bone density.
- Medication: If osteoporosis is advanced, doctors may prescribe bone-strengthening medications such as bisphosphonates.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing smoking and alcohol consumption, getting adequate sunlight exposure, and maintaining a healthy weight can lower osteoporosis risk.
Osteoporosis is a serious health issue, and early diagnosis can help prevent fractures and complications. Individuals showing signs of osteoporosis should consult Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Orthopedics, Endocrinology, or Internal Medicine. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and an active lifestyle can help minimize the effects of osteoporosis.