Breast Imaging
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer worldwide after lung cancer. Early detection significantly increases survival rates.
Some Procedures Used in Breast Imaging:
Low-Dose, Three-Dimensional (3D) Mammography
Also known as tomosynthesis, this imaging technique complements 2D mammography by providing more precise images. X-ray is used to capture images from various angles, allowing the exact location of lesions to be identified in 3D.
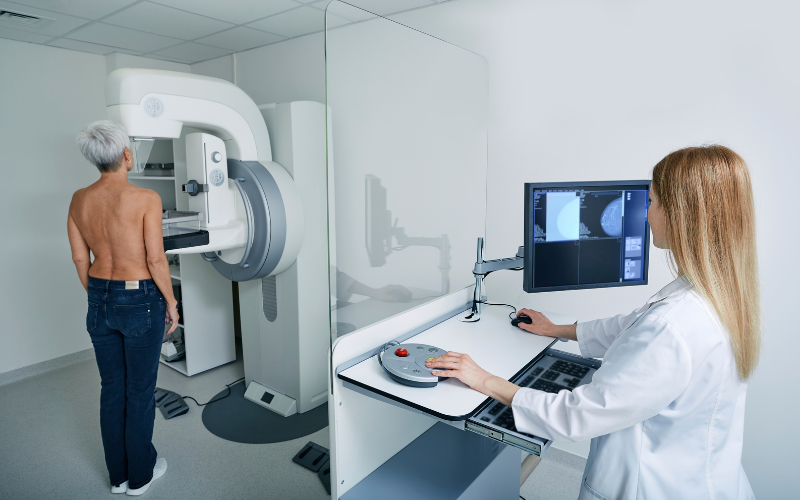
Digital Mammography
Utilizes low-dose X-rays for the screening and diagnosis of breast pathologies. Recommended regularly for women over 40 and high-risk groups, this method facilitates early diagnosis and treatment.
Breast Ultrasound
A safe method used to evaluate suspicious areas detected during physical exams or mammography, particularly in women with dense breast tissue.
Breast MRI
Evaluates small lesions that may be missed by mammography using magnetic resonance imaging. This radiation-free method is essential for detailed imaging in women with a family history of breast cancer or genetic predisposition.
MRI-Guided Breast Biopsy
Uses magnetic resonance imaging to accurately localize lesions that may not be detected by mammography or ultrasound and perform biopsies. This method ensures rapid and accurate diagnosis, allowing early treatment initiation.
Stereotactic Breast Biopsy
A technique used to biopsy suspicious areas that cannot be evaluated by ultrasound, guided by mammography. This method provides a fast and highly accurate diagnosis.